Important Points:
- Common causes of lower back pain and their risk factors
- Lifestyle habits and body mechanics affecting back health
- Preventive tips to protect your lower back
- Treatment options for pain caused by various factors
Understanding the Root Causes of Lower Back Pain
What is Lower Back Pain?
Lower back pain is one of the most common health complaints worldwide, affecting people across all ages and lifestyles. It can range from a mild ache to severe, debilitating discomfort. While occasional pain may stem from temporary strain, chronic lower back pain often has underlying causes that, once identified, can be managed or prevented. Understanding the root of your lower back pain is the first step toward finding relief and improving your quality of life.
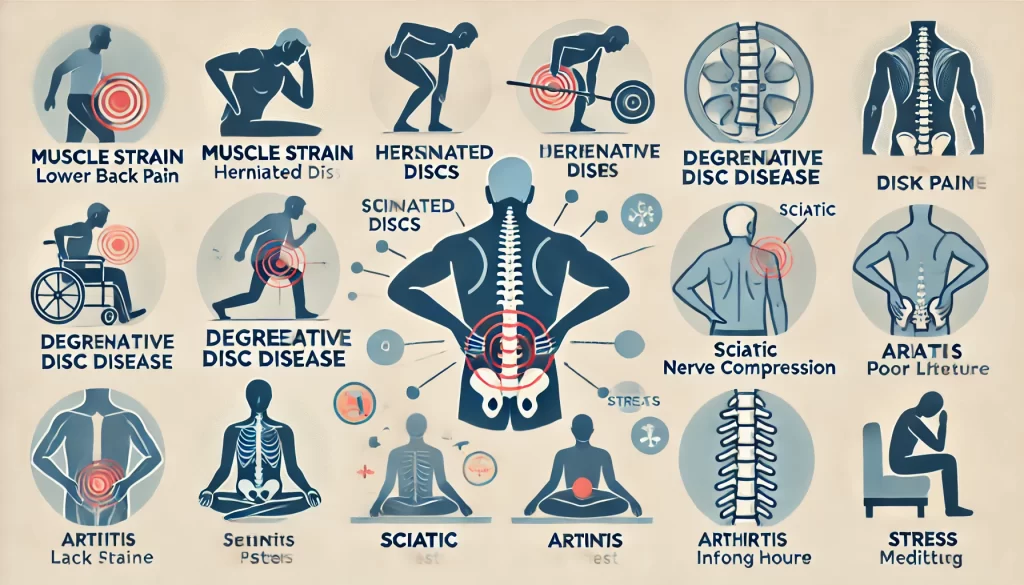
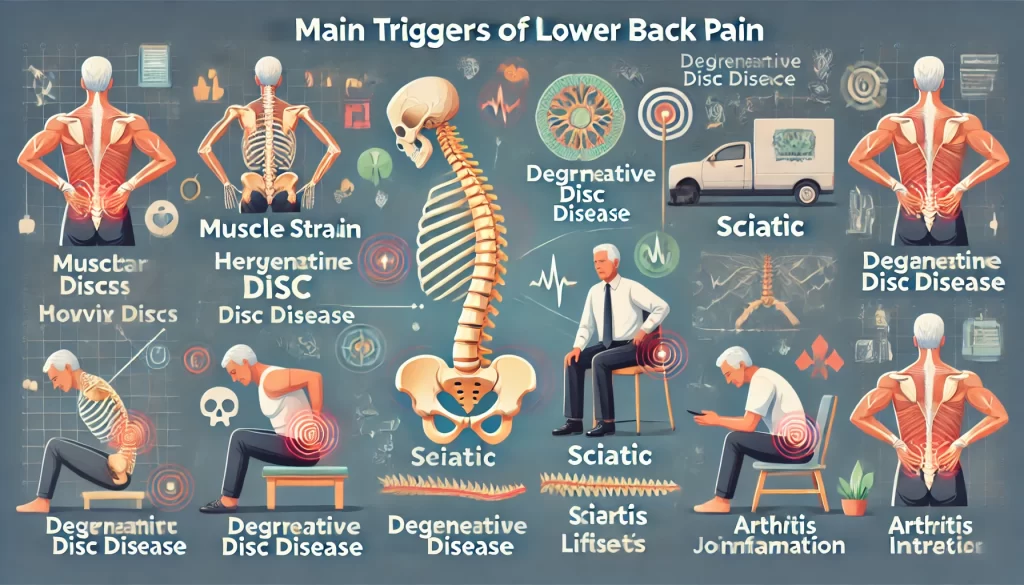
Common Causes of Lower Back Pain
- Muscle Strain and Ligament Sprain
- Explanation: One of the most frequent causes of lower back pain is a strain in the muscles or ligaments. Overuse, sudden movements, or lifting heavy objects can lead to muscle strain, causing pain and stiffness in the lower back.
- Prevention Tips: Be mindful of your posture when lifting heavy items. Always use your legs to lift rather than your back, and avoid sudden twisting motions.
- Herniated or Bulging Discs
- Explanation: Your spine is cushioned by discs that act as shock absorbers. A herniated or bulging disc occurs when the soft interior of a disc protrudes, often compressing nearby nerves. This condition can result in pain, numbness, or even muscle weakness.
- Prevention Tips: Regular core-strengthening exercises can help support your spine and reduce the risk of disc issues. Avoid prolonged sitting, especially in positions that don’t support your back properly.
- Degenerative Disc Disease
- Explanation: As people age, the discs in the spine naturally begin to break down or degenerate, losing their flexibility and cushioning ability. This can lead to conditions like osteoarthritis, which causes pain and stiffness.
- Prevention Tips: Maintain a healthy weight to avoid extra pressure on the spine, and consider low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling to keep your back strong without strain.
- Sciatica
- Explanation: Sciatica is caused by compression of the sciatic nerve, which runs from the lower back down to the legs. This compression, often from a herniated disc or bone spur, causes radiating pain that can extend down through the legs.
- Prevention Tips: Incorporate stretching exercises into your daily routine to keep your muscles flexible and reduce nerve compression risk.
- Poor Posture
- Explanation: Slouching, sitting in a poor position, or maintaining an incorrect posture while standing or walking can place unnecessary strain on the lower back. Over time, poor posture weakens back muscles and increases the risk of pain.
- Prevention Tips: Practicing good posture, using ergonomic furniture, and taking regular breaks if you sit for long periods can greatly reduce lower back strain.
- Sedentary Lifestyle
- Explanation: Lack of regular exercise leads to weak muscles, especially in the core, which is essential for supporting your spine. A sedentary lifestyle can also contribute to weight gain, adding further strain to the lower back.
- Prevention Tips: Even light exercises like walking, stretching, and core workouts can strengthen your back muscles and reduce the risk of lower back pain.
- Arthritis
- Explanation: Conditions like osteoarthritis cause the cartilage between joints to wear down, leading to pain and stiffness. Arthritis in the lower back, particularly in the facet joints, can lead to chronic lower back pain.
- Prevention Tips: While arthritis can’t be entirely prevented, managing inflammation with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and, if necessary, medication can help reduce its impact.
- Stress and Anxiety
- Explanation: While it might seem unrelated, stress can cause muscle tension, particularly in the lower back area. Chronic stress can also increase your sensitivity to pain, making any lower back discomfort feel worse.
- Prevention Tips: Practice stress-relieving techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or engaging in hobbies you enjoy. Physical activity also helps to manage stress and reduce muscle tension.
Preventive Tips for Lower Back Health
Here are some proactive steps to help protect your lower back from pain:
- Exercise Regularly: Strong back and abdominal muscles help support the spine and reduce strain. Consider low-impact exercises to avoid overloading your back.
- Stay Mindful of Posture: Whether sitting, standing, or lifting, maintaining good posture is essential for back health.
- Take Frequent Breaks: If you sit for long periods, stand up and stretch regularly to relieve back tension.
- Choose Supportive Footwear: Proper footwear can prevent imbalances and distribute weight evenly, reducing pressure on the spine.
- Manage Weight: Maintaining a healthy weight minimizes stress on your back and decreases the risk of conditions that contribute to pain.
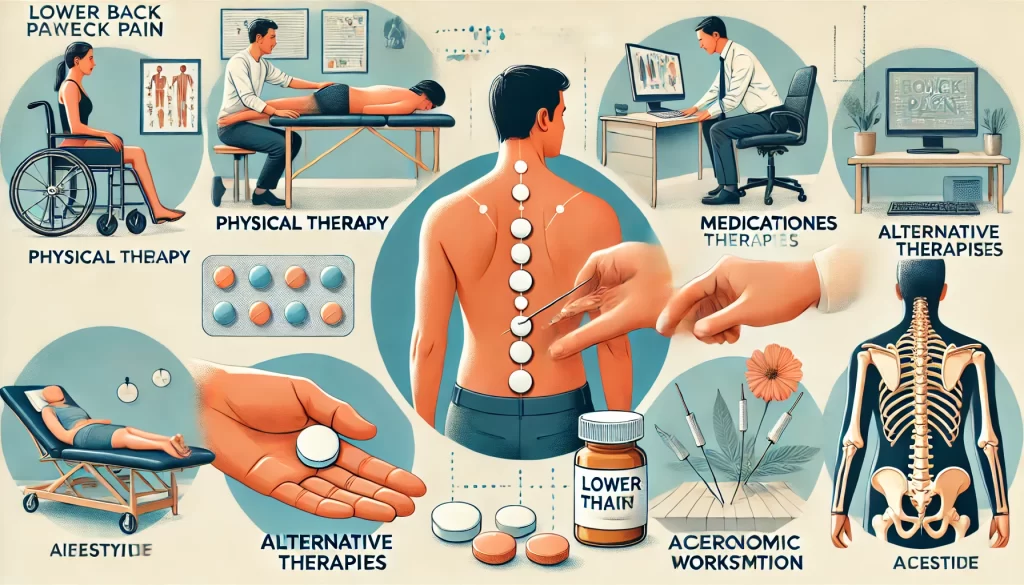
Treatment Options for Lower Back Pain
If you’re already experiencing lower back pain, various treatments are available, depending on the cause:
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can guide you in exercises to strengthen back muscles and improve flexibility.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, like ibuprofen, can help reduce inflammation and pain. In more severe cases, your doctor may recommend stronger medications.
- Alternative Therapies: Options such as acupuncture, chiropractic adjustments, and massage therapy may provide relief by targeting muscle tension and enhancing circulation.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Small changes, like avoiding prolonged sitting or switching to an ergonomic workstation, can make a big difference.
Conclusion: Protecting Your Lower Back from Pain
Understanding the causes of lower back pain is a crucial step toward prevention and effective management. While some causes, such as age-related degeneration, are unavoidable, you can significantly reduce your risk through proper posture, regular exercise, and mindful lifestyle choices. With consistent effort, you can safeguard your lower back and enjoy a more active, pain-free life.