Important Points:
- Common causes of middle back pain in women
- Unique factors and lifestyle habits contributing to middle back pain
- Preventive exercises and lifestyle adjustments
- Treatment options for managing and alleviating middle back pain
Middle Back Pain in Women: Causes, Prevention, and Relief
Why Do Women Experience Middle Back Pain?
Middle back pain, also known as thoracic back pain, is less common than lower back pain but can be equally disruptive. The middle back, located between the shoulder blades and just above the lower back, plays a crucial role in supporting the upper body. Pain in this area can result from various lifestyle factors, anatomical differences, or even underlying health conditions. For women, hormonal changes, body mechanics, and certain conditions may contribute uniquely to middle back discomfort.
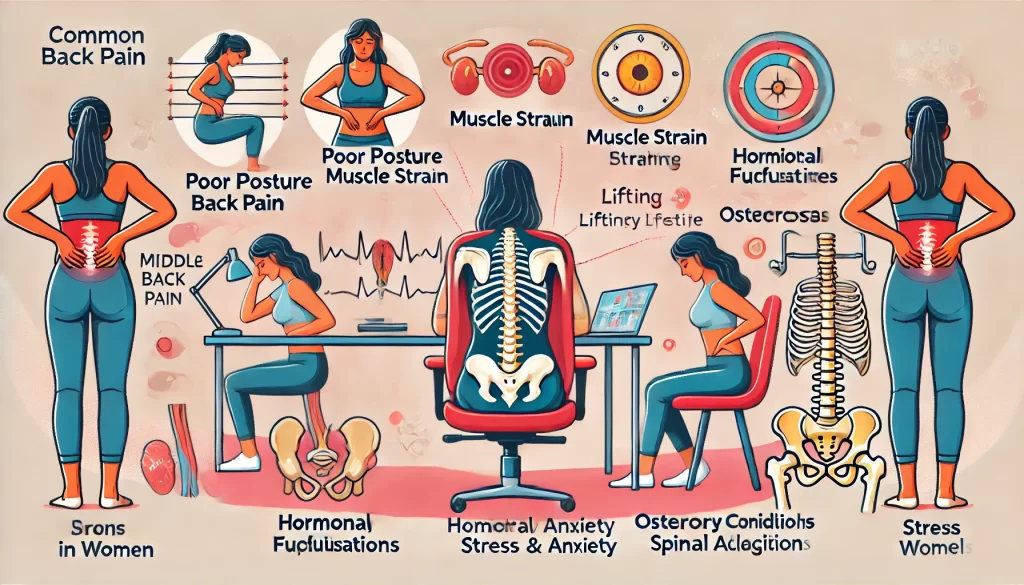
Common Causes of Middle Back Pain in Women
- Poor Posture and Extended Sitting
- Explanation: Poor posture is a leading cause of middle back pain, particularly for women who spend extended periods sitting or working at a desk. Slouching or leaning forward can strain the muscles and ligaments in the middle back, leading to discomfort over time.
- Prevention Tips: Be mindful of posture by using ergonomic chairs, adjusting desk height, and practicing core-strengthening exercises. Taking regular breaks to stretch or walk can also help.
- Muscle Strain from Lifting and Carrying
- Explanation: Carrying heavy bags, lifting children, or moving heavy items can strain the muscles in the middle back, especially if not done with proper technique. Women are often multitasking, leading to lifting items without correct body mechanics.
- Prevention Tips: Use lifting techniques that engage the legs and avoid twisting your body. If you carry bags frequently, try to balance the weight on both sides or consider using a backpack.
- Hormonal Fluctuations
- Explanation: Hormonal changes, especially during the menstrual cycle or menopause, can affect joint and muscle health. For some women, hormonal shifts can lead to increased muscle tension, particularly in the middle back.
- Prevention Tips: Gentle stretching, regular exercise, and staying hydrated can help alleviate muscle tension associated with hormonal changes. Yoga poses that stretch the middle back can also be beneficial.
- Sedentary Lifestyle
- Explanation: A sedentary lifestyle can weaken back muscles, reducing support for the spine and increasing the risk of pain. Sitting for long periods without movement can lead to stiffness and tension in the middle back.
- Prevention Tips: Incorporate daily activities like walking, light stretching, or low-impact exercises to keep muscles active. Even brief movement breaks can help prevent stiffness in the back.
- Stress and Anxiety
- Explanation: Emotional stress can cause muscle tension, particularly in the upper and middle back. Women are more likely to experience chronic stress, which can lead to prolonged muscle tightness and discomfort.
- Prevention Tips: Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or regular physical activity to manage stress and reduce muscle tension in the middle back.
- Osteoporosis
- Explanation: Osteoporosis is a condition where bones become brittle and weak, increasing the risk of fractures. Women are particularly prone to osteoporosis, especially after menopause, and this can contribute to pain in the middle back due to weakened vertebrae.
- Prevention Tips: Regular weight-bearing exercises, a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, and bone density screenings can help maintain bone health and reduce the risk of fractures.
- Spinal Conditions
- Explanation: Conditions like scoliosis, kyphosis, or herniated discs can cause pain in the middle back. Scoliosis, for instance, is a sideways curvature of the spine that affects women more commonly than men. This misalignment puts additional strain on the back muscles.
- Prevention Tips: Early detection and physical therapy can help manage conditions like scoliosis. Stretching and strengthening exercises, as well as periodic check-ups, are crucial for spine health.
Exercises and Lifestyle Adjustments to Prevent Middle Back Pain
- Thoracic Spine Stretch: This stretch helps relieve tension in the middle back. Sit upright, cross your arms over your chest, and gently rotate your upper body from side to side, holding for a few seconds on each side.
- Foam Rolling: Foam rolling can target sore muscles in the middle back and release built-up tension. Lie on a foam roller placed horizontally under your shoulder blades and gently roll up and down.
- Core Strengthening: Core exercises, like planks, help support the spine and reduce strain on the back. By strengthening the core, you relieve some of the load on your back muscles.
- Yoga and Pilates: Both yoga and Pilates improve flexibility, strengthen muscles, and can provide targeted relief for middle back pain. Poses like “Child’s Pose” or “Cat-Cow” are particularly effective for stretching the spine.
- Regular Movement Breaks: For those who work at desks or sit for long periods, taking frequent breaks to stand, stretch, and move around can make a big difference in middle back comfort.
When to Seek Medical Help
If middle back pain becomes persistent or severe, it may indicate a more serious underlying condition. Women should consider seeing a healthcare provider if they experience:
- Pain that doesn’t improve after several weeks
- Tingling, numbness, or weakness in the arms or legs
- Pain that worsens with movement or interferes with daily activities
- Signs of osteoporosis, such as unexplained fractures
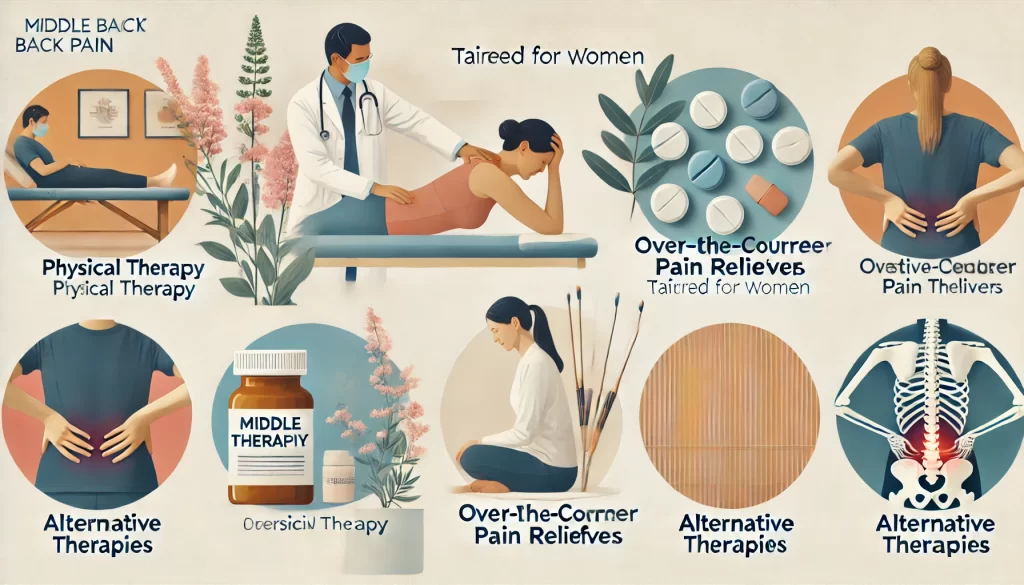
Treatment Options for Middle Back Pain in Women
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can create a targeted exercise plan to strengthen muscles and improve flexibility. Therapy sessions may include gentle stretching, posture correction, and mobility exercises.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. Always consult a doctor before using these medications regularly.
- Alternative Therapies: Techniques like acupuncture, chiropractic adjustments, and massage therapy may help by increasing blood flow and releasing tension.
- Stress Management: Managing stress is essential for long-term relief. Techniques such as meditation, mindfulness practices, and deep breathing exercises can lower overall stress and reduce muscle tension in the back.
Conclusion: Managing Middle Back Pain for a Better Quality of Life
Middle back pain can significantly affect a woman’s quality of life, but many causes are manageable with the right approach. By understanding the potential triggers, practicing preventive measures, and making lifestyle adjustments, women can reduce middle back pain and enhance overall well-being. Taking proactive steps, such as regular exercise, ergonomic adjustments, and stress management, will help maintain a healthier, more comfortable back.